Mpox symptoms and transmission are on high alert with hospitals and other testing centers designated as India, Know what is monkeypox and symptoms, how to prevent…
21 august 2024
Amid growing concerns over the global spread of monkeypox, India’s Union Health Ministry has issued directives to increase vigilance at all international airports and land ports, particularly those bordering Bangladesh and Pakistan. The measure aims to identify and isolate any incoming international travelers exhibiting symptoms of empox, a viral disease caused by the monkeypox virus, which belongs to the orthopoxvirus genus. According to information, the Ministry’s proactive steps are part of a comprehensive strategy to prevent the virus from entering and spreading in the country.Although no cases of Mpox or Monkeypox have been reported in India so far, the government has ensured preparedness in case of an outbreak. Also, the government has asked hospitals to prepare isolation wards for patients.

What is Monkeypox:
Monkeypox is a zoonotic disease caused by a virus. The symptoms of this disease, although mild, are similar to those of the orthopox virus infection, smallpox, which was eradicated from the world in 1980. This disease is mainly seen in Central and West African countries. The disease was first identified in monkeys in 1958 and the first human infection was diagnosed in 1970 in a 9-year-old boy in the Republic of Congo. The disease is caused by monkeypox virus and can spread from animals to humans and from one infected person to another.
How it spreads:
The disease can be spread through contact with the body fluids of infected animals. The disease is found in squirrels, rats and various monkeys. People living near forested areas are at risk of viral infection when they come into contact with infected animals. In humans, the disease is spread through inhalation. Exposure to wounds, body fluids and bedding used by an infected person. Since vaccination against smallpox has stopped, low immunity makes people vulnerable to the infection.
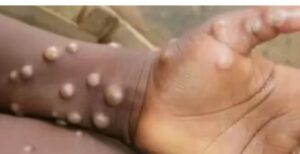
Symptoms of monkeypox:
The incubation period for monkeypox virus is usually between 6 and 13 days. But in some cases, the incubation period is found to be between 5 to 21 days. Symptoms may last 2 to 4 weeks. Cases of monkeypox have a low mortality rate.
Common symptoms include fever, severe headache, swollen lymph nodes near the groin, back pain, muscle aches and lethargy. After 13 days of fever, skin rashes – mostly like watery blisters – appear on the face, hands, feet, palms, genital area and eyes. The severity of the illness varies from person to person. Depends on their general health, immunity and other underlying infections. Complications of this disease include broncho-pneumonia, sepsis, encephalitis and corneal infection. Asymptomatic manifestations of the disease are not yet known.
Remedy or treatment:
Because it is a viral infection, there is no cure for monkeypox. However, treatment is required to avoid concurrent infections/complications. Treatment should be started as soon as symptoms appear to avoid complications and long-term effects of the disease. Vaccination against monkeypox is already available.
Prevention: Avoid unprotected contact with infected animals or burial of dead animals. One should also avoid contact with one’s own flesh and body fluids. Meat products should be thoroughly cooked before consumption. The main cause of spread in humans is close contact with infected individuals. Just as precautions are taken to prevent Covid infection, similar precautions need to be taken while caring for a monkeypox patient.